
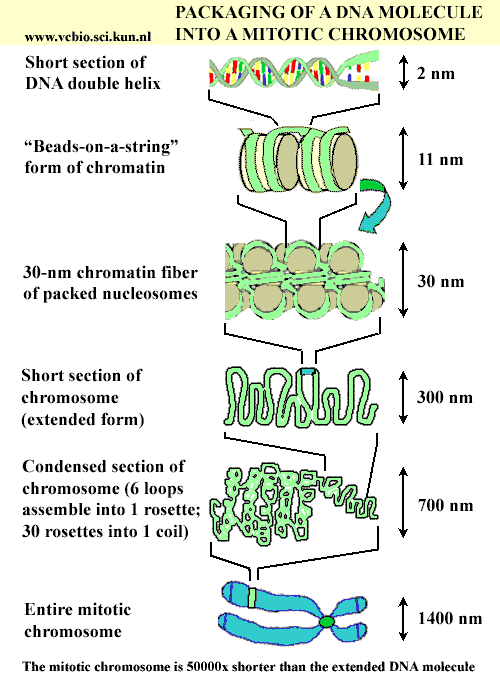
”Ĭhromatin is the masses of fine fibers comprising the chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell in a nondividing state. The influence of the inactive X chromosome expression in off-spring is known as “lyonization. It has since been verified that the Barr body is inactive, preventing females from transcribing double the genes found on X chromosomes. Lyon to hypothesize in 1962 that it was inactive. Its dense, compact form led researcher M. In 1949 a condensed X chromosome (termed the Barr body), which is visible at interphase (nondividing periods) in the body cells of female mammals was first observed. Regions of DNA that are not transcribed clump together in the nucleolus. Certain strands of chromatin are always found in specific locations. These structures are optimised to withstand the physical forces imposed on the DNA during replication and division.Ĭhromatin is thought to have a very well organized layout in the nucleus. During meiosis, chromatin further coils onto scaffold proteins and forms the classic chromosomes known from karyotypes. The compact structure of chromomeres is an efficient means of storing long stretches of DNA. However, the 30nm fiber can easily be unwound to the beads on a string structure for transcription. The beads on a string formation can be further coiled into a filament known as a 30nm chromatin fiber which is more compact and is found in DNA that is less actively being transcribed.

This formation optimises access to DNA for transcription. The nucleosomes are found in a “beads on a string ” formation, with 20 to 60 base pairs of “linker DNA ” between nucleosomes. The core nucleosome is comprised of a segment of DNA wrapped around an octomer of histones forming ball-like strucutres. ” Chromatin granules that form the chromosomes are known as chromomeres.Ĭhemically, chromatin fibers consist of DNA and several types of proteins found in the cell nucleus (nucleoproteins): core histones, histone H1 and scaffold proteins. When the chromatin condenses during cell division, the resulting structures are called chromosomes, which means “colored bodies. They named this material “chromatin, ” using the Greek word chroma, which means color. Flemming found that in cells stained with a basic dye, the granular material in the nucleus turned a bright color. Chromatin is present only in cells with a nuclear membrane it is not found in prokaryotic cells (e.g., bacteria) that lack a nucleus.Ĭhromatin was named by Walther Flemming in 1882 who examined cells using a light microscope. During cell division (mitosis or meiosis) chromatin masses together into thick shortened bodies which are then called chromosomes. Chromatin refers to the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and associated proteins packaged together in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell in a nondividing state.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
